Data Science¶
What is data science?¶
Data Science is a set of processes and systems to extract knowledge or insights from data, either structured or unstructured (Wikipedia). For the purpose of this document consists of managing, analyzing and visualizing data in support of machine learning workflow.
What is machine learning?¶
Machine learning: Artificial intelligence machines that improve their predictions by learning from large amounts of input data.
Main idea: Learning = estimating underlying function 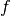 by mapping data attributes to some target value.
by mapping data attributes to some target value.
Training set: A set of labeled examples 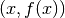 where
where 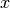 is the input variables and the label
is the input variables and the label 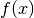 is the observed target truth.
is the observed target truth.
Goal: Given a training set, find approximation 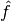 of
of 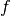 that best generalizes, or predicts, labels for new examples. Best is measured by some quality measure, for instance: error rate, sum squared error.
that best generalizes, or predicts, labels for new examples. Best is measured by some quality measure, for instance: error rate, sum squared error.
Image:ML.png
Why machine learning¶
Difficulty in writing some programs
- Too comples (facial recognition)
- Too much data (stock market predicions)
- Information only available dynamically (recommendation system)
Use of data for improvement
- Humans are used to improving based on experience (data)
A lot of data available
- Product recommendations
- Fraud detection
- Facial recognition
- Language understanding
Types of machine learning¶
Supervised learning¶
A “teacher” provides training examples, each with correct label. Regression y classification.
Unsupervised learning¶
Correct label not available for training examples, must find patterns in data (e.g. using clustering). Example: grouping customers according to what books and movies they like.
Reinforcement learning¶
Not told what action is correct, but given some reward or penalty after each action in a sequence. Example: learning how to play soccer
semi-supervised learning,
Data matters¶
image:data.png
- Unleash the business value in data collected
- Prepare you to do data science projects and to implement production systems
- Predict future events based on past data leading to proactive change than reactive
The Data Science and ML workflow¶
Image:workflow.png
Concepts:
Dataset
Trainig set versus test set
Feature = attribute = independent variable = predictor
Label = target = outcome = class = dependent variable = response
Dimensionality = numer of features
Model selection
Key Issues in ML¶
Data quality¶
Consistency of the data, Accuracy of the data, noisy data, missing data, outliers in the data, Bias, Variance
Model quality¶
Image:modelquality.png
Overfitting¶
Failure to generalize: Model performs well on trainig set but poorly on test set.
Typically indicates that model is too flexible for amount of training data.
Flexibility allows it to “memorize” the data, including noise.
Corresponds to high variance - small changes in the training dat lead to big changes in the results
Underfitting¶
Failure to capture important patterns in the training data set.
Typically indicates that model is too simple or there are too few explanatory variables.
Not flexible enough to model real patterns
Corresponds to high bias - the results show systematic lack of fit in certain regions
Computation speed and scalability¶
Use distributed computing systems like Amazon SageMaker or Amazon EC2 instances for training in order to: increase speed, solve prediction time complexity, solve space complexity.