Analytics Services¶
AWS serverless data analytics pipeline reference architecture
Amazon Athena¶
Amazon Athena is an interactive query service that makes it easy to analyze data in Amazon S3 using standard SQL expressions. Athena is serverless, so there is no infrastructure to manage, and you pay only for the queries you run. Athena is easy to use. Simply point to your data in Amazon S3, define the schema, and start querying using standard SQL expressions. Most results are delivered within seconds. With Athena, there?s no need for complex ETL jobs to prepare your data for analysis. This makes it easy for anyone with SQL skills to quickly analyze large-scale datasets.
Athena is serverless, so there is no infrastructure to set up or manage, and you pay only for the queries you run. Athena scales automatically?executing queries in parallel?so results are fast, even with large datasets and complex queries.
Athena helps you analyze unstructured, semi-structured, and structured data stored in Amazon S3. Examples include CSV, JSON, or columnar data formats such as Apache Parquet and Apache ORC. You can use Athena to run ad-hoc queries using ANSI SQL, without the need to aggregate or load the data into Athena.
AWS Data Pipeline¶
Amazon Elasticsearch¶
Amazon EMR¶
Amazon EMR provides a managed Hadoop framework that makes it easy, fast, and cost-effective to process vast amounts of data across dynamically scalable Amazon EC2 instances. It securely and reliably handles a broad set of big data use cases, including log analysis, web indexing, data transformations (ETL), machine learning, financial analysis, scientific simulation, and bioinformatics. You can also run other popular distributed frameworks such as Apache Spark, HBase, Presto, and Flink in Amazon EMR, and interact with data in other AWS data stores such as Amazon S3 and Amazon DynamoDB.
AWS Glue¶
Amazon Kinesis streaming data platform¶
Amazon Kinesis streaming data platform consists of Kinesis Data Firehose, Kinesis Data Streams, Kinesis Video Streams, and Amazon Kinesis Data Analytics.
Amazon Kinesis Data Firehose¶
Amazon Kinesis Data Firehose is the easiest way to load streaming data into data stores and analytics tools. It can capture, transform, and load streaming data into Amazon S3, Amazon Redshift, Amazon Elasticsearch Service (Amazon ES), and Splunk, enabling near real-time analytics with existing business intelligence tools and dashboards you?re already using today.
It is a fully managed service that automatically scales to match the throughput of your data and requires no ongoing administration. It can also batch, compress, and encrypt the data before loading it, minimizing the amount of storage used at the destination and increasing security.
For Amazon ES destinations, streaming data is delivered to your Amazon ES cluster, and it can optionally be backed up to your S3 bucket concurrently.
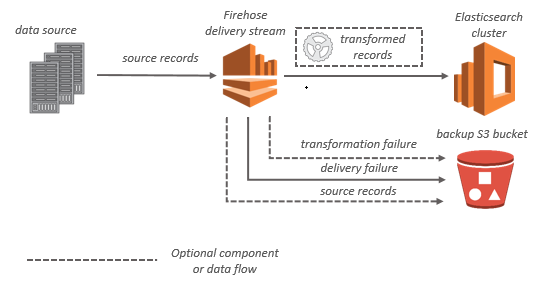
Amazon Kinesis Data Firehose with Amazon ES destination
Kinesis Data Streams¶
The vocabulary for data streaming is putting records into a data stream and reading the stream back. You can have multiple shards that provide throughtput. You can create as many shards as you need with a data stream, they are not created dynamically.
Let’s image a producer want to send a record, then in order to Kinesis Data Streams what shard to use, you tag the record with the partition key. This partition key is very similar to the message group identifier in a SQS FIFO queue. The process is the following:
- The producer calls put record.
- The Kinesis Data Streams service needs to decide to which shard this record is going to be appended. This decision is done through hashing. Each shard owns a subset of hashes. Kinesis calculates the hash for the message partition value and finds out to which shard it belongs.
- Amazon Kinesis Data Streams stores the record and synchronously replicates data across three availability zones, providing high availability and data durability.
- It is return an OK back to the producer.
Image an scenario where:
- A producer sends a record to the appropriate shard in terms of its shard.
- The stream stores the record durably to its correspondent shard.
- There is a networking problem when the producer was calling send message.
- The producer gets a timeout. It doesn’t know if Kinesis got the record or it didn’t.
- The producer retry the send.
- Kinesis calculate again the record hash and sends it to the same shard as the previous version. There is going to be a duplicate.
When you need more throughput and you have already data in your data stream, you can do a shard split. You select one of the shards and split it into two: you divide the hash space of one the shards into two hash subspaces. You can scale the throughput as much as you want by adding as many shards as you want. Resharding means that it does not influence existing data, the records get appended to the new shards if applicable. You do not have to decide which shards are needed to be splitted, it is done automatically by Kinesis.
A consumer is responsible for deciding from which shard is going to consume and which record to consume. The first action that the consumer should do is to ask Kinesis what shards are available. Then it will a pick a shard and start reading from an iterator. As a consequence, with Kinesis Data Streams there is consumer affinity: a consumer read all the records from a shard. It is easy to perform analysis of consecutive entries.
When you consume from a data stream, you are not deleting any record. This means that you can start multiple applications consuming from the same stream, like a fanout pattern, doing some analysis on the data stream.
If the number of shards increases, the complexity of the code of the consumers increases as well. The consumer is responsible for keeping track who is reading, from which shard, check the progress of reading, … Because of that, instead of using directly Kinesis API for consuming, it is recommend to use existing client-side libraries called Kinesis Client Library (KCL). This library does the complex management of shards: electing who is reading from each shard, of tracking progress of your reads, and allows to focus on the code needed to process the data in the records.
A new shard iterator is returned by every GetRecords request (as NextShardIterator), which you then use in the next GetRecords request (as ShardIterator). Typically, this shard iterator does not expire before you use it. However, you may find that shard iterators expire because you have not called GetRecords for more than 5 minutes, or because you’ve performed a restart of your consumer application.
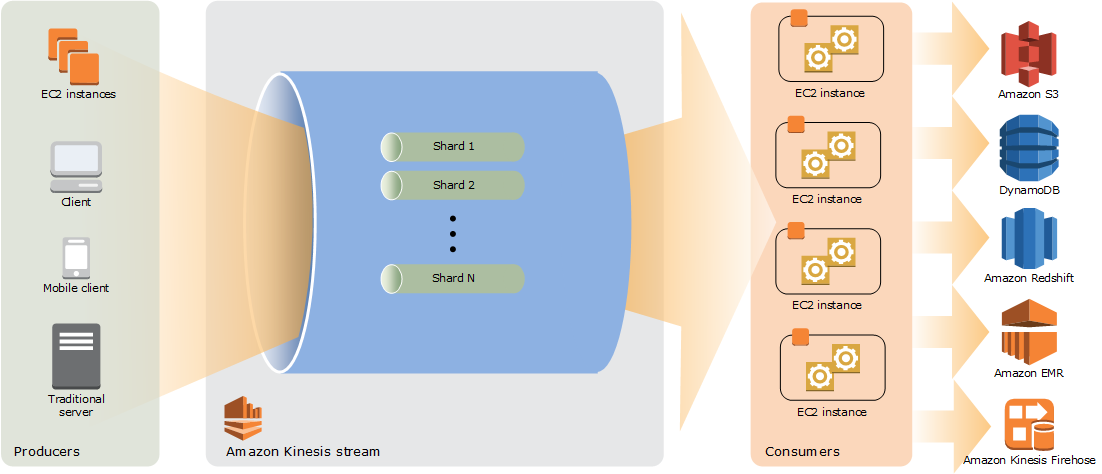
Kinesis Data Streams architecture
Kinesis Data Streams supports changes to the data record retention period of your stream. A Kinesis data stream is an ordered sequence of data records meant to be written to and read from in real-time. Data records are therefore stored in shards in your stream temporarily.
The time period from when a record is added to when it is no longer accessible is called the retention period. A Kinesis data stream stores records from 24 hours by default to a maximum of 168 hours (7 days).
Resharding¶
Amazon Kinesis Data Streams supports resharding, which lets you adjust the number of shards in your stream to adapt to changes in the rate of data flow through the stream. Resharding is considered an advanced operation.
There are two types of resharding operations: shard split and shard merge. In a shard split, you divide a single shard into two shards. In a shard merge, you combine two shards into a single shard. Resharding is always pairwise in the sense that you cannot split into more than two shards in a single operation, and you cannot merge more than two shards in a single operation. The shard or pair of shards that the resharding operation acts on are referred to as parent shards. The shard or pair of shards that result from the resharding operation are referred to as child shards.
Splitting increases the number of shards in your stream and therefore increases the data capacity of the stream. Because you are charged on a per-shard basis, splitting increases the cost of your stream. Similarly, merging reduces the number of shards in your stream and therefore decreases the data capacity?and cost?of the stream.
If your data rate increases, you can also increase the number of shards allocated to your stream to maintain the application performance. You can reshard your stream using the UpdateShardCount API. The throughput of an Amazon Kinesis data stream is designed to scale without limits via increasing the number of shards within a data stream.
Amazon Kinesis Data Analytics¶
Amazon Kinesis Data Analytics is the easiest way to analyze streaming data, gain actionable insights, and respond to your business and customer needs in real time. Amazon Kinesis Data Analytics reduces the complexity of building, managing, and integrating streaming applications with other AWS services. SQL users can easily query streaming data or build entire streaming applications using templates and an interactive SQL editor. Java developers can quickly build sophisticated streaming applications using open source Java libraries and AWS integrations to transform and analyze data in real-time.
Amazon Kinesis Data Analytics takes care of everything required to run your real-time applications continuously and scales automatically to match the volume and throughput of your incoming data. With Amazon Kinesis Data Analytics, you only pay for the resources your streaming applications consume. There is no minimum fee or setup cost.